Feasibility study highlights how co-locating high-tech agriculture with data centers can expand job creation, boost energy efficiency, and drive regional food system resilience.
A new feasibility report reveals an emerging opportunity to align two of Virginia’s target sectors—data centers and controlled environment agriculture (CEA)—through strategic co-location. This report was released by non-profit Resource Innovation Institute (RII) in partnership with the Institute for Advanced Learning and Research (IALR) and GO Virginia Region 3.
The report, Co-locating Data Centers and Greenhouses: A Feasibility Report, explores how Southern Virginia can adapt global best practices to create a new model for regional innovation and economic development. Highlighting Agriport A7 in the Netherlands as a leading example, the study outlines how co-locating these industries can unlock resource efficiencies, create high-quality jobs, and enhance community resilience.
“Virginia is strategically building a strong foundation for Controlled Environment Agriculture, driven by innovation and strengthened through public-private collaboration, to position our Commonwealth as a national leader,” said Secretary of Agriculture and Forestry Matt Lohr. “This report shows the potential to create high-quality agricultural jobs in rural Virginia while delivering significant revenue gains for local communities.”
“As data infrastructure expands and CEA continues to gain traction in Virginia, there’s a unique opportunity to plan ahead for smart, synergistic development,” said Derek Smith, Executive Director of Resource Innovation Institute and co-author of the report. “We’re excited to offer this analysis as a roadmap for how Virginia can lead the nation in co-location innovation.”
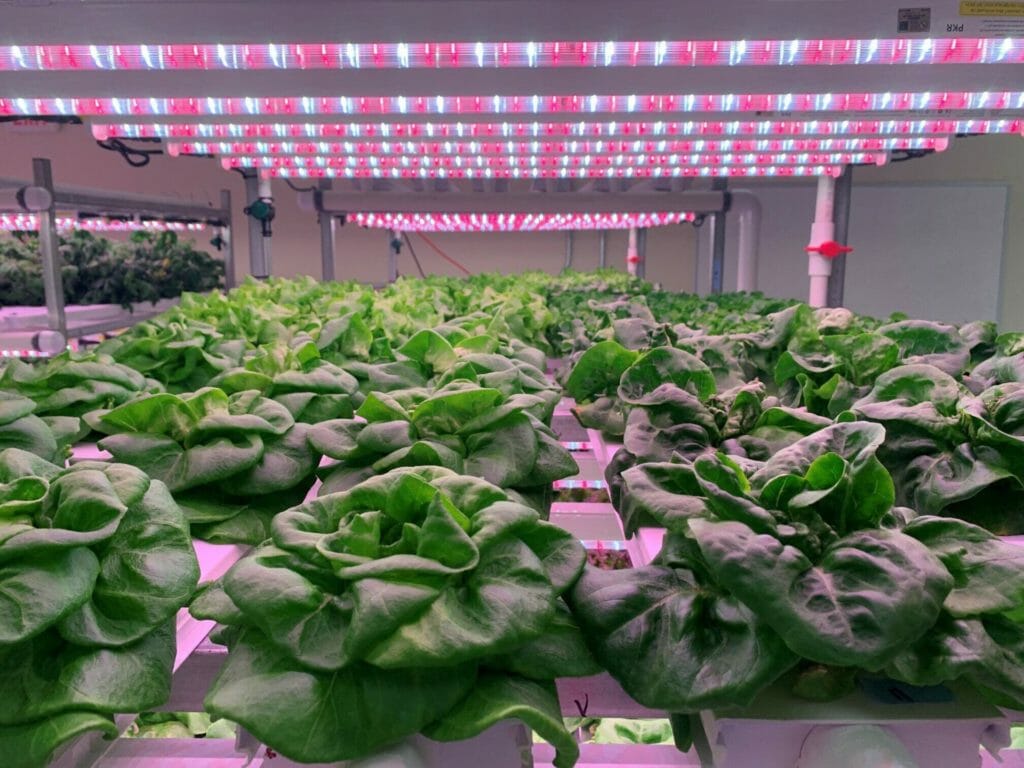
The study presents a vision for clustered development zones where data centers and greenhouses share infrastructure, such as heat, CO₂, and energy, to reduce costs and improve efficiency. This clustering model, often seen in the Netherlands and Canada, offers a more competitive development plan compared to isolated facilities.
“We are pleased to collaborate with RII and IALR on this pioneering analysis,” said R. Bryan David, Chair of GO Virginia Region 3 Council. “Co-location between data centers and CEA operations represents an actionable, strategic opportunity to strengthen the regional economy while aligning with our long-term development goals.”
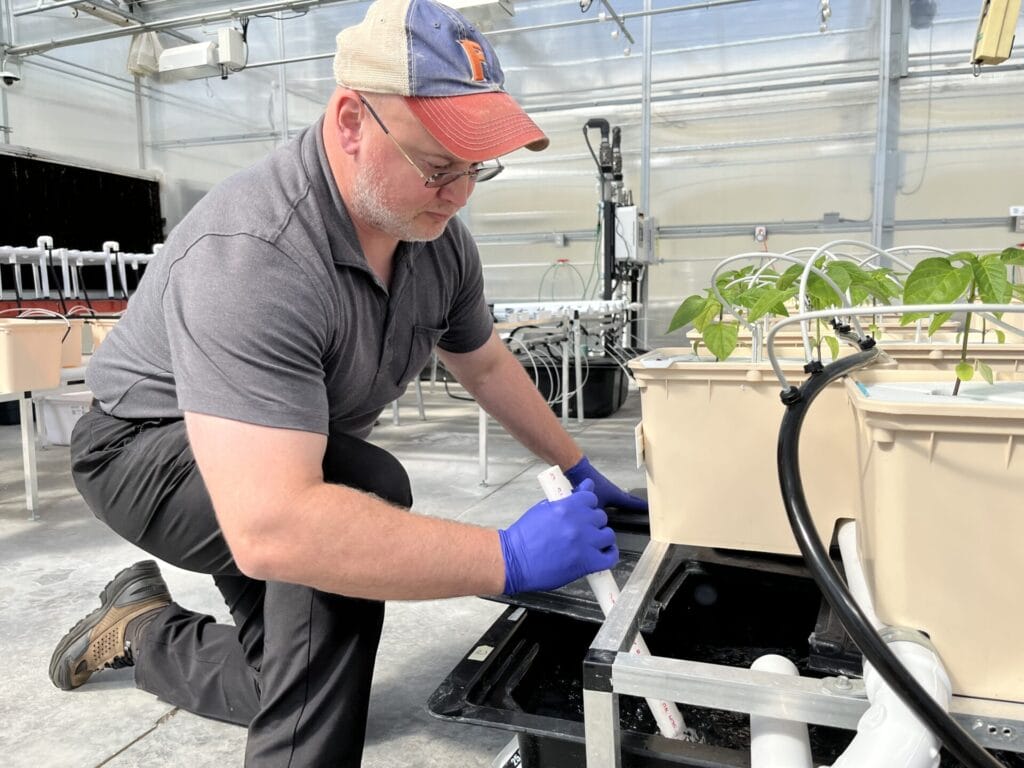
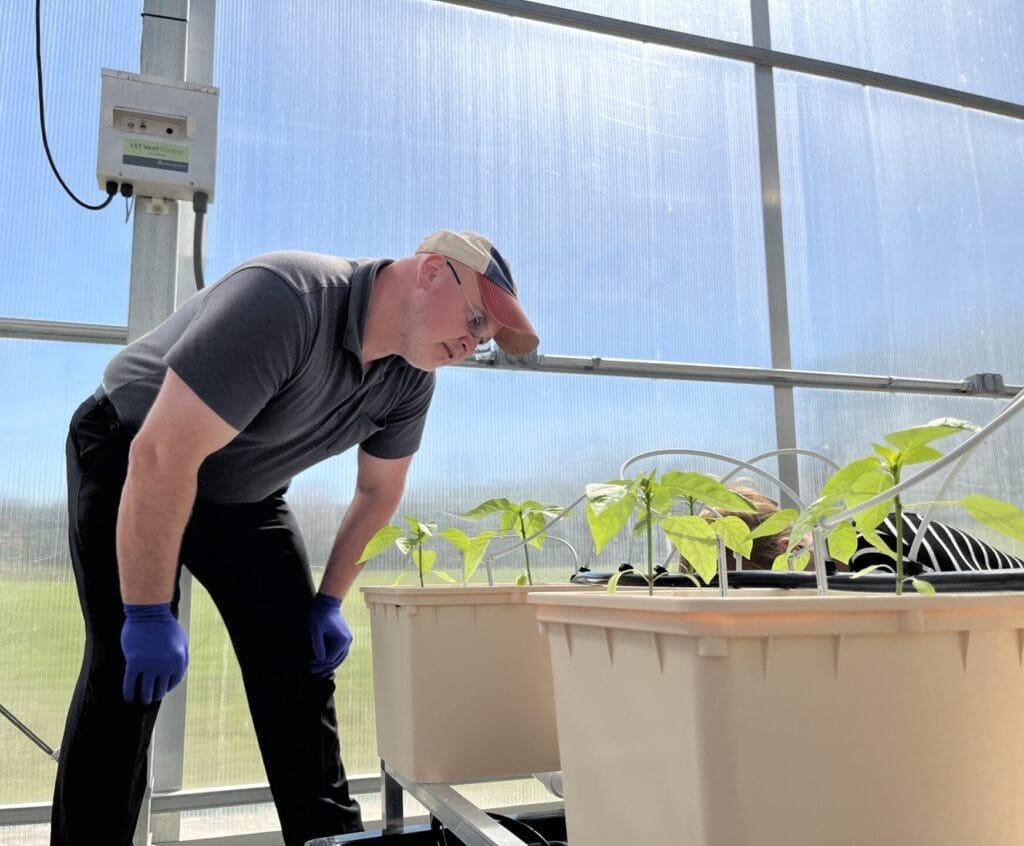
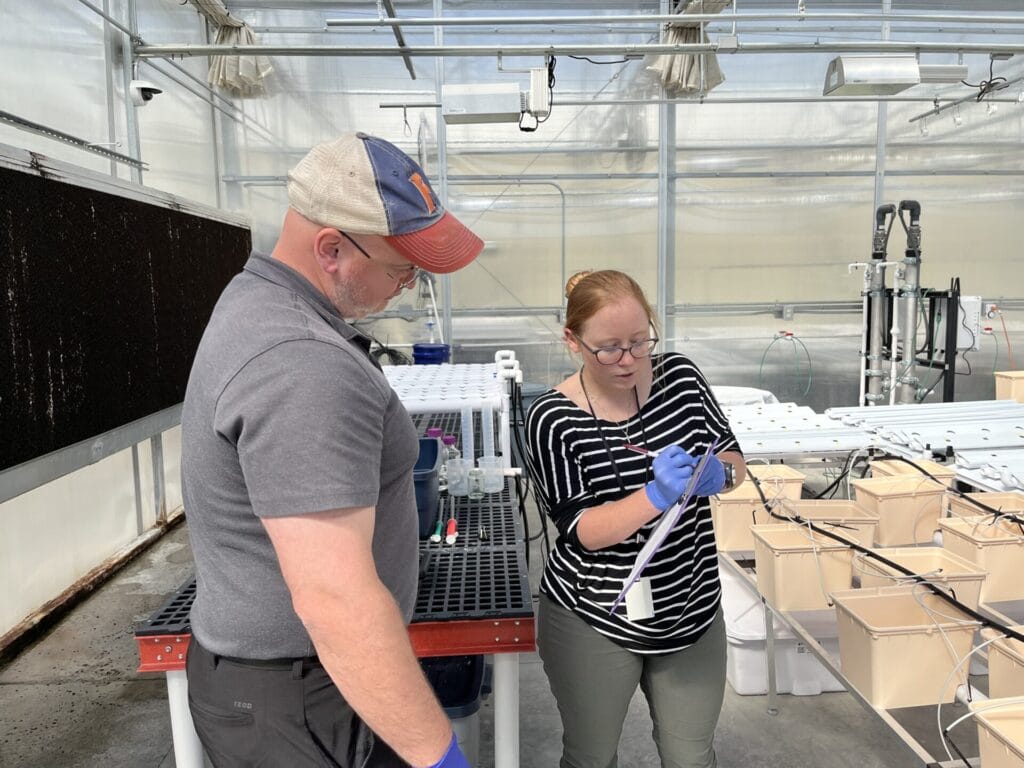
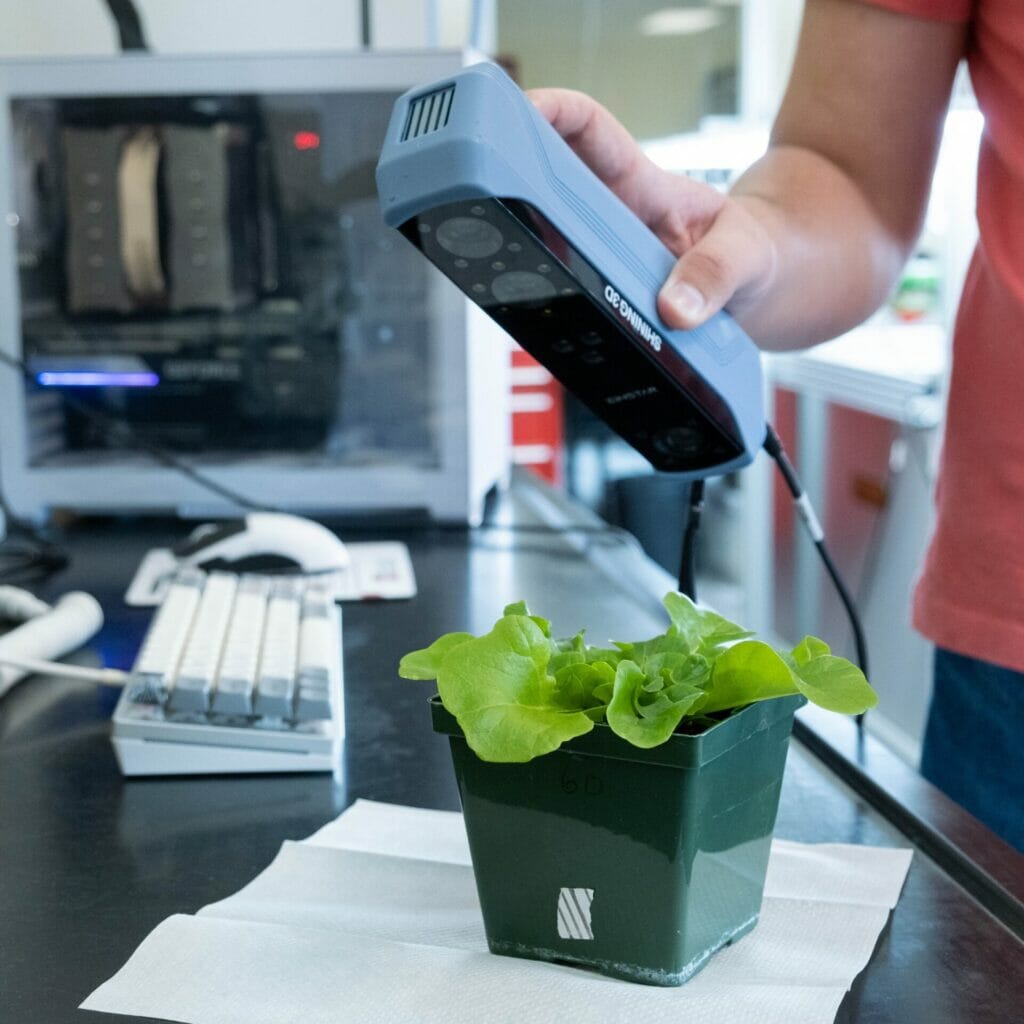
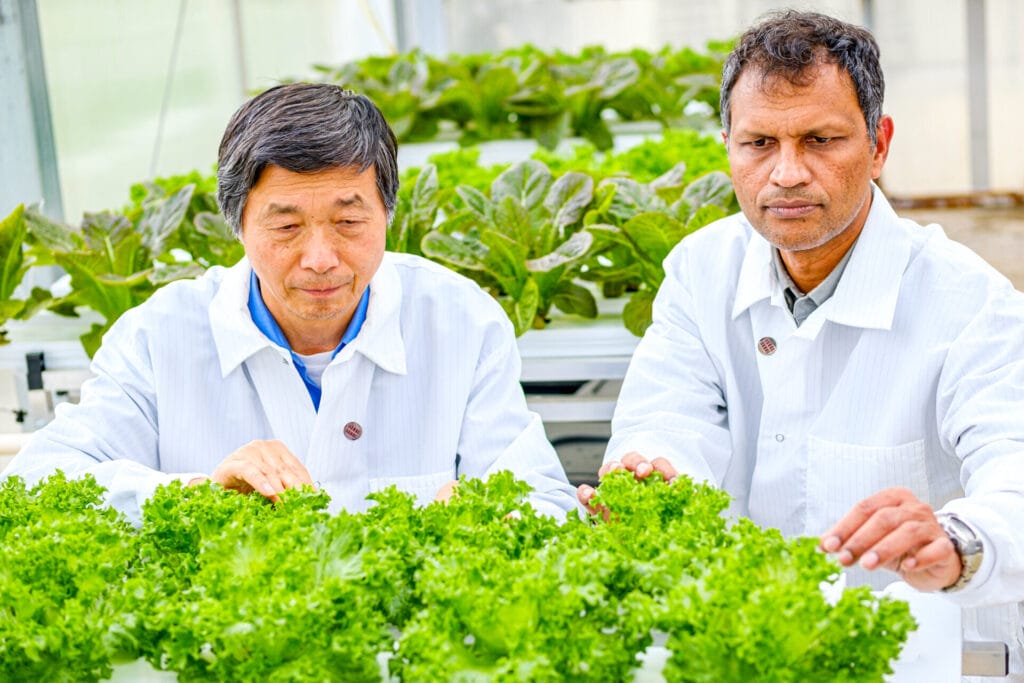
This opportunity comes at a time of notable momentum for the CEA industry in Virginia, with Danville emerging as a hub of activity due to research assets like the CEA Innovation Center, robust broadband infrastructure, and ready industrial parks.
“Controlled environment agriculture continues to grow across Southern Virginia,” said Dr. Scott Lowman, Vice President of Applied Research at the Institute for Advanced Learning and Research. “This model of co-location can position our communities to compete nationally while delivering long-term economic and workforce benefits.”
Key Findings from the Report:
- Waste heat from data centers can be repurposed to benefit greenhouse operations by providing energy, heating, and CO₂ for plant growth.
- CEA offers strong job creation potential, with each 65-acre greenhouse supporting 140–270 jobs, significantly more than a typical data center.
- Industrial clusters unlock shared infrastructure and economic multipliers, making co-located development more competitive than standalone facilities.
- Southern Virginia is uniquely positioned to pilot this concept due to its broadband access, industrial sites, and assets like the CEA Innovation Center and robust workforce training programs
The study recommends evaluating specific co-location sites, launching a demonstration project, and building a coalition to coordinate public-private investment. Drawing on decades of greenhouse management experience, report co-author Rob Eddy, RII’s Horticulturist, emphasizes the importance of aligning infrastructure planning with agricultural and data sector growth to maximize economic and environmental returns.
This research aligns with RII’s broader work through the CEA Accelerator, a U.S. Department of Energy-supported initiative advancing energy- and water-efficient agriculture. By integrating co-location strategies into regional development, the report offers a roadmap for communities like Southern Virginia to pursue resilient food systems, efficient industrial design, and long-term job creation.
Contact: Derek Smith, Executive Director
Email: derek@resourceinnovation.org
About Resource Innovation Institute (RII):
Resource Innovation Institute (RII) is a non-profit shaping the future of food, energy, water, and data systems. Partnering with governments, utilities, industry leaders, and research institutions, RII develops strategies and tools that scale controlled environment agriculture (CEA) as a solution to global food and resource challenges.
Building on work with the U.S. Department of Energy, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, USDA, and state agencies, RII is designing Farm Parks, regional resilience hubs that unite high-tech food production, circular resource sharing, and data infrastructure to achieve economies of scale.
About the Institute for Advanced Learning and Research (IALR)
The Institute for Advanced Learning and Research serves Virginia as a regional catalyst for economic transformation with applied research, advanced learning, manufacturing advancement, conference center services and economic development efforts.
About GO Virginia Region 3
GO Virginia Region 3 works to grow and diversify the economy of Southern Virginia by investing in regional projects that drive innovation, workforce readiness, and business growth.
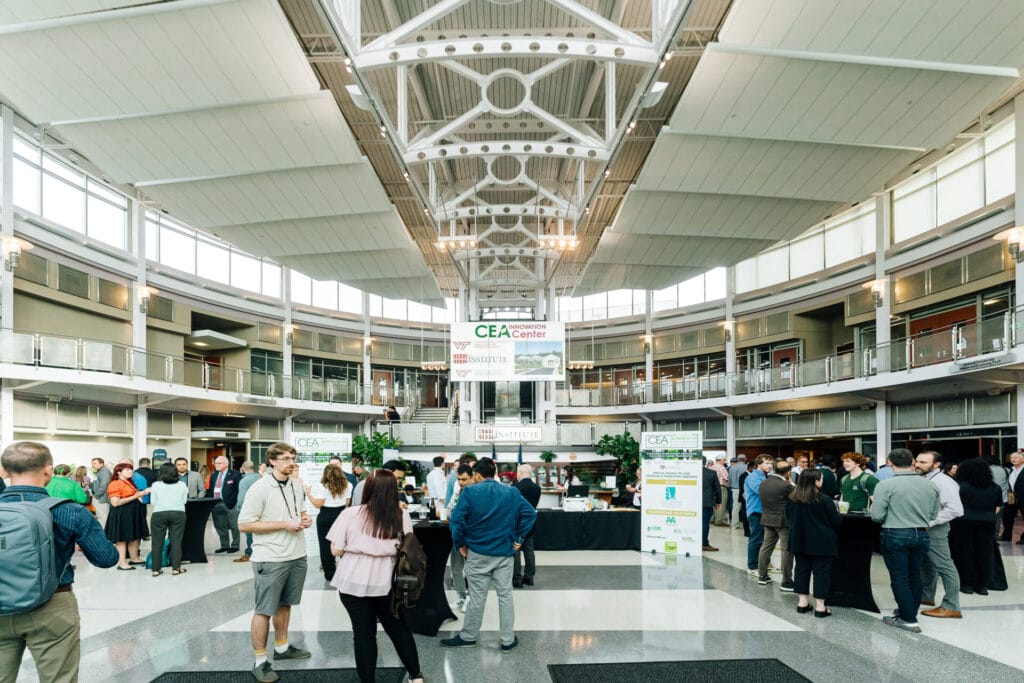



























 Virginia October 1-2, 2024 Edition Brings Academia and Industry Together For Collaboration, Innovation
Virginia October 1-2, 2024 Edition Brings Academia and Industry Together For Collaboration, Innovation